If you are reading this, your scraper likely just hit a brick wall.
In standard web protocols (RFC 7231), a 405 Method Not Allowed response indicates that the server recognizes the target URL, but rejects the specific HTTP method used (such as GET, POST, or PUT). Typically, this happens when a developer tries to POST a form to a read-only resource.
However, in the context of web scraping, this definition is often misleading. Modern anti-bot systems hijack this status code to block automated traffic without revealing the true reason for the rejection.
This guide explains why your script is failing and how to bypass the “False 405” using both code-level fixes (Python) and infrastructure-level fixes (Octoparse).
Quick Fix
If you’re getting a 405 error, first check:1. You are using the correct HTTP method (GET vs POST)
2. The endpoint is not read-only
3. Your server/router config allows the method
If all of that looks correct, and especially if the same URL works in Chrome but not in your script, keep reading.
Why You’re Getting a 405 Method Not Allowed Error (3 Real Causes)
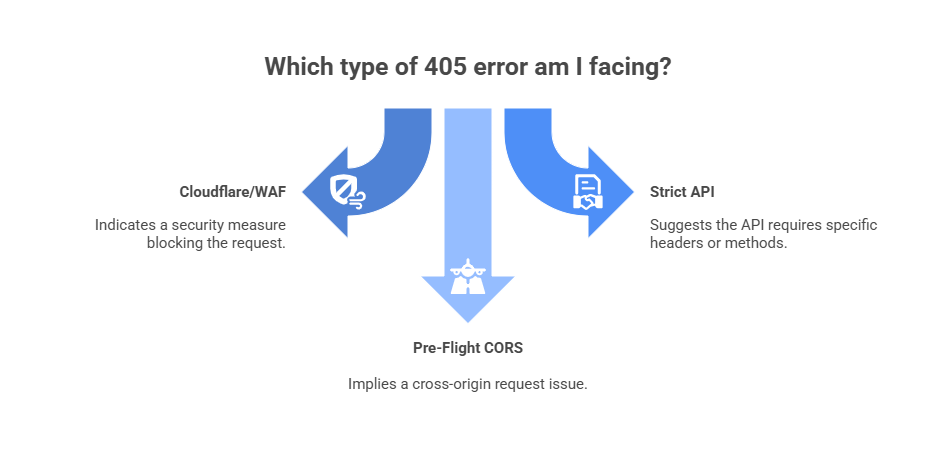
Before you start rewriting your headers, you need to diagnose which “version” of the 405 error you are facing.
1. Cloudflare 405 Error (Bot Detection Disguised as Method Not Allowed)
This is the most common cause for web scrapers. WAFs (Web Application Firewalls) like Cloudflare, Akamai, or Datadome often return a 405 error instead of a 403 (Forbidden) when they detect a bot.
- The Mechanism: The WAF analyzes your TLS fingerprint and User-Agent. If it sees a Python script (e.g., python-requests/2.28) or a Headless Chrome instance without proper masking, it rejects the request method to confuse your retry logic.
- The Diagnosis: You get a 405 error on the main homepage (e.g., https://site.com), which should always accept a simple GET request.
Before attempting to patch your code, you need to confirm if the block is behavior-based (rate limits) or identity-based (TLS fingerprinting).
If your script works locally but fails in production, or works for 50 requests and then throws a 405, you are most likely dealing with a compromised digital fingerprint.
2. 405 Method Not Allowed Due to Wrong HTTP Method (GET vs POST)
This is the only time the error message is telling the truth. You are trying to scrape a login endpoint or a hidden API (XHR), and you sent a GET request when the server explicitly requires a POST request with a JSON payload.
- The Diagnosis: Check the Network Tab in Chrome DevTools. If the failed request corresponds to a form submission or “Load More” button, you likely used the wrong HTTP verb.
3. 405 Error Caused by CORS Preflight (OPTIONS Request)
If you are scraping via a browser automation tool (like Selenium or Puppeteer) that injects JavaScript, you might trigger a CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) pre-flight check.
The target server sees a request from a “null” origin (your script) and rejects the OPTIONS method with a 405.
How to Tell If a 405 Error Is a Bot Block (Checklist)
Run this 5-point diagnostic to confirm if you are facing a WAF (Web Application Firewall) block:
- Does the URL work in Chrome?
- Does it fail only after multiple requests?
- Does it work locally but fail on a server?
- Does the response contain Cloudflare headers?
- Does waiting 15 minutes fix it?
Part 1: How to Fix 405 Method Not Allowed in Python Requests
If you are maintaining your own scraper, you need to mimic a “human” browser handshake perfectly to bypass the WAF.
Step 1: Audit Your Headers (The “User-Agent” Fix)
The default User-Agent for the Python requests library is an immediate red flag to any WAF.
Don’t do this:
codePython
Do this:
codePython
Tip: If you are scraping a site hosted on Azure, a 405 error can specifically indicate that you are using a forbidden verb (like PUT or DELETE) on a read-only endpoint.
Step 2: Handle Redirections Manually
Some sites redirect http:// to https://. During this redirect, a POST request can be stripped down to a GET request by some libraries, causing a method mismatch on the final URL.
- The Fix: Enable allow_redirects=True or manually trace the redirect chain to ensure you are hitting the final destination URL.
Part 2: Octoparse Handles 405 Errors Caused by Bot Protection
If you are spending more time debugging 405 errors than analyzing data, your problem isn’t “code”—it’s infrastructure.
At this point, you have two options:
- Patch your scraper manually (headers, proxies, CAPTCHA solvers)
- Use a browser-based scraping infrastructure that handles this automatically
Octoparse bypasses these errors by using a legitimate browser stack with built-in anti-blocking tech. Here is how it handles the specific causes of a 405 error.
1. Handling Cloudflare and JavaScript-Based Challenges
If your Python script hits a Cloudflare 405, it’s often because a background CAPTCHA (like Turnstile) failed to load. Python requests cannot execute JavaScript, so it fails instantly.
Note: Libraries like requests cannot run JavaScript, so the challenge never completes and the server responds with a misleading error.
Octoparse uses a modified Chromium browser that automatically handles many Cloudflare and JavaScript-based anti-bot challenges by running in a real browser environment, which allows the page to load normally before data extraction begins. It handles the JavaScript challenge before the request is sent, preventing the 405 error from triggering.
Read more: How Octoparse Handles CAPTCHA Solving
2. Auto-Rotating User Agents & Proxies (The “Soft Ban” Fix)
When a 405 error is a “Soft Ban,” it means your IP address has been flagged. No amount of header tweaking will fix this; you need a new identity.
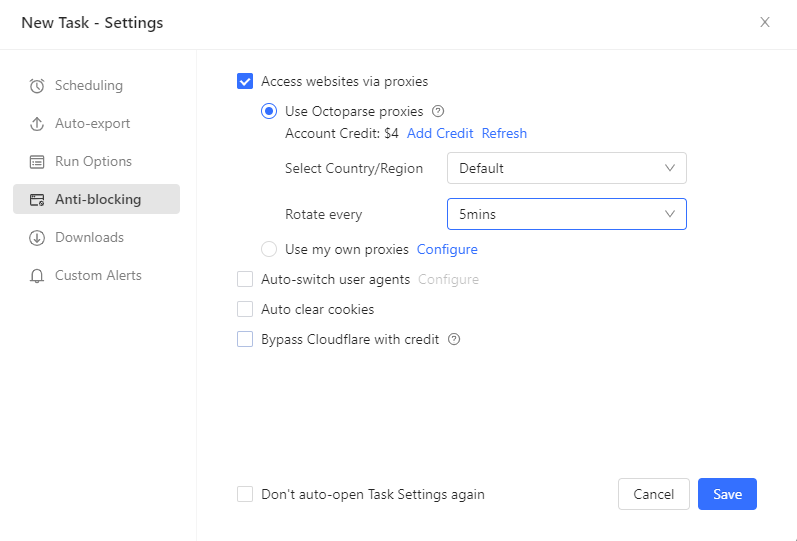
- Octoparse allows you to enable Auto IP Rotation.
- User Agents: It uses real browser fingerprints and automatically varies user agents to avoid static, script-like identities.
- Residential Proxies: If a 405 hits, Octoparse can automatically switch to a high-quality Residential IP, presenting the request as coming from a different browsing session and IP location.
- Read more: Residential Proxies for Scraping
This combination helps mitigate temporary blocks that cannot be resolved by modifying headers alone.
3. Configuring Automatic Retry Logic for 405 Errors
Instead of stopping a task when a 405 error occurs, Octoparse allows users to configure conditional retry behavior at the workflow level.
- The Feature: “Retry Condition”
- How to set it up:
- Go to the Task Settings.
- Set a customized rule: “If HTTP Response Code = 405” OR “If page text contains ‘Method Not Allowed'”…
- Action: “Switch Proxy and Retry.”
- The Result: The task can be configured to retry automatically, optionally switching proxies before reloading the page. You get 100% of the data, even if 10% of the requests were initially blocked.
In practice, this allows a scraping task to continue running even if a portion of requests initially fail due to temporary blocking.
Turn website data into structured Excel, CSV, Google Sheets, and your database directly.
Scrape data easily with auto-detecting functions, no coding skills are required.
Preset scraping templates for hot websites to get data in clicks.
Never get blocked with IP proxies and advanced API.
Cloud service to schedule data scraping at any time you want.
FAQ: Understand 405 Errors in Context
Q: What is error 405 in Azure Web App scraping?
A: If you see a 405 error specifically on Azure-hosted sites, it often means the web.config file on the server has blocked specific verbs (like PUT, DELETE, or even HEAD) for security. Ensure your scraper is strictly using GET for page loads and POST only when submitting forms.
Q: Why do I get a 405 Error in Python but not in Chrome?
A: This confirms it is a bot detection issue. Your Chrome browser sends “User-Agent”, “Sec-Ch-Ua” (Client Hints), and “Accept-Language” headers that prove you are human. Your Python script sends none of these. To fix it, you must replicate these headers or use a browser-based tool like Octoparse.
Q: Can a 405 Error be a temporary block? How long does a 405 block last?
A: Yes. Many anti-scraping systems use “Method Not Allowed” as a temporary “cool-down” block for 10-15 minutes if you request too fast. If you wait 20 minutes and it works again, you need to slow down your scraping speed or use IP Rotation to spread your requests.
Conclusion
Stop fighting the firewall.
You can write Python scripts to handle headers, buy proxy pools, and integrate CAPTCHA solvers manually. Or you can Download Octoparse and let the infrastructure handle the 405 errors for you.




