With the help of web scraping, individuals and businesses are now able to access huge amounts of data from a wide range of sources in diverse industries. The New York Times, one of the most reputable media institutions in the world, is a good source of web scraping. You may gather tons of information from it, including news articles, blog posts and comments by using web scraping. Following that, this data may be applied to a variety of initiatives involving machine learning, sentiment analysis, research, news aggregation, and other data-driven insights.
The New York Times
The New York Times (NYT) is a well-known American newspaper. The organization has gained a superb reputation for its extensive reporting and diverse content covering a wide range of topics, such as politics, science, technology and more. Its digital platform is well-known for being user-friendly and data-rich, making it an excellent resource for finding fast, accurate, and high-quality information. The Times is a great target for web scraping because of its unmatched coverage of local, national, and international news.
Why People Scrape the New York Times
People scrape The New York Times for several reasons. Researchers and academicians conduct text analysis or review trends for historical research. Companies, especially those involved in media monitoring, reputation management, or sentiment analysis, take advantage of web scraped data for deriving business intelligence. It also helps journalists and content curators who use news aggregation to organize their content more efficiently. All things considered, online scraping ensures data-driven decisions based on accurate and timely information, giving companies and people a major competitive advantage.
What Data You Can Scrape from the New York Times
News Articles: As a fundamental part of any news outlet, the quality and comprehensiveness of news articles are of prime importance. You can extract diverse data such as the main text body, headline, author, published date, and URL of all articles. This enables an in-depth view of various sectors like politics, economy, technology, health and many more. The acquired data provides valuable insights into the subject matter, writing styles, and positional leanings of articles across different categories.
Comments: Public participation is a vital aspect of contemporary journalism, offering insights into collective sentiments and individual reactions. By scraping user comments and reactions to articles, we can gauge public sentiment on a variety of issues. This provides a unique perspective on how news events and stories are received and interpreted by readers, allowing for a multilayered understanding of public discourse regarding current affairs.
Images: Visual elements significantly enhance the narrative potential of news articles. By scraping images associated with the articles, including their captions and potential metadata, one obtains not just ancillary information, but also an understanding of how visual media is used to augment story presentation. This can be a rich source of data for visual analyses and understanding the context of the reportage more comprehensively.
Tags and Categories: News articles come with specific tags and fall under certain categories, serving as a quick reference to the content and context of the article. Scrapping these tags and categories can offer a useful perspective on trending subjects and can help identify patterns in article themes over time, with potential implications for understanding reader interests and preferences.
Author Information: Authorial data forms an essential subset of news data. Scrapping information about authors such as their designation, bio, and other articles can facilitate a deeper analysis of the perspectives and biases that may color news-reporting. It can also provide insights into patterns of authorship, recurring themes in specific authors’ works, and their impact on public engagement.
Three Easy Steps to Scrape the New York Times
Octoparse is a powerful web scraping tool designed to access and extract diverse data types from various website structures. It has a distinct advantage because of its complex capabilities, which include support for AJAX, JavaScript, cookies, sessions, and redirects. It is good for both non-coding people and experts since it doesn’t require any coding skills to operate. The program stands out for its capacity to efficiently and dependably gather data from The New York Times, despite common scraping challenges. Let’s now explore the detailed instructions for utilizing this powerful tool to its fullest potential.
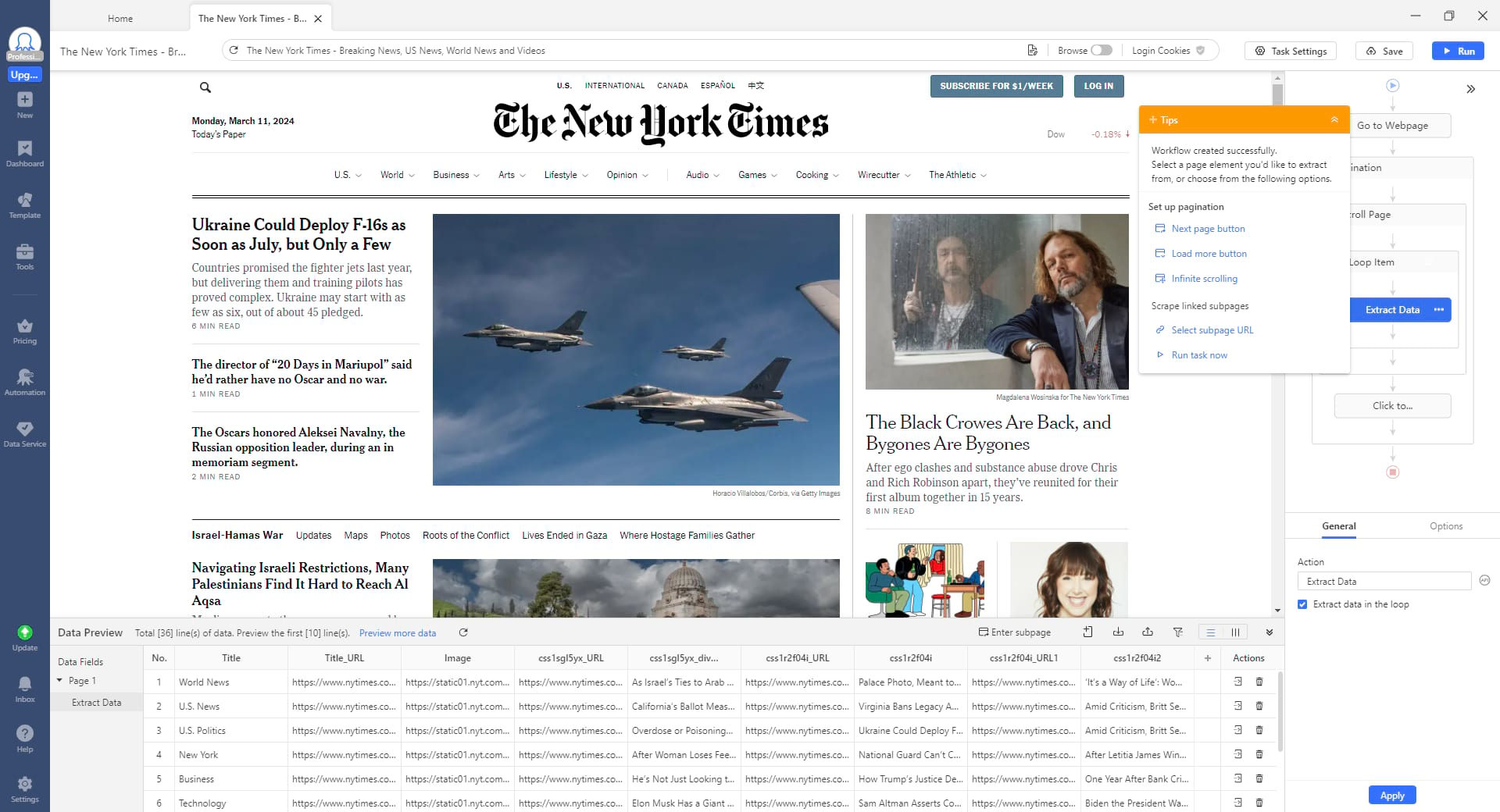
Step 1: Build a new task
In Octoparse, enter the New York Times’ URL or URLs that you want to scrape. Then, click “Start” to create a new article or news scraping task.
Step 2: Select data and build a scraper
Once the web page finishes loading, click the ‘auto-detect’ on the tip panel to identify data that can be scraped or manually select the required data if the auto-detect function does not accurately identify the desired information. Click “Create workflow” when all desired news data has been specified. A workflow will then appear on the right hand side. It demonstrates all of the scraper’s functions and actions.
Click on each action to see whether the scraper performs as needed. You may also add new activities to make sure it works well for you.
Step 3: Extract and the New York Times data
Click the “start” button to run the scraper after verifying all the information. The scraper will start collecting news or article data from the New York Times based on the settings you established earlier. Once the data scraping process is finished, the collected information can be downloaded in Excel, CSV spreadsheet or any other format.
Tips: Here are some other news scraping resources like scraping CNN, how to build effective content aggregation and more that may help you with your news and articles web scraping!
wrap up
In a nutshell, the method of using Octoparse to scrape the New York Times is highly valuable as it eradicates the laborious task of manual data collection, providing prompt and accurate data for informed decision making. Web scraping serves as a robust strategy for data collection from the New York Times and other news sources. However, it’s important to abide by the regulations of the website, including robots.txt, copyright laws, and ensuring ethical use of the collected data. For more comprehensive scraping operations, consider the application of advanced features that tools like Octoparse offer, including IP rotation, task scheduling, and the usage of regular expressions, among others. Enjoy your web scraping experience!